Proteomics 2022
ABOUT THE CONFERENCE
11th International Conference on Genomics , Proteomics & Bioinformatics Is going to be held in Singapore City , Singapore on August 22-23, 2022
International conference on Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics 2022 is hosted by EuroSciCon and it focuses on the large-scale study of Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics. We are inviting Business delegates, Industrial Leaders, Protein Researchers, gene researchers, Scientists, CEO's and R&D Heads from Industries, Directors, Head of departments, Professors and Students from Academia in the research of genomics, proteomics & Bioinformatics. The conference will be a programme to globalize one research, to share scientific exposure, to gain knowledge on new technologies and rules. The conference will be conducted on August 22-23 at Singapore City. We invite financers and exhibitor to display your products to our participants and make it reach the public through them. We request you to apply for this opportunity to make the world a better place to live in.
WHAT IS NEW?
This conference on Genomics, proteomics & Bioinformatics includes international attendee workshops, lectures and symposia, including a designated registration area, a refreshment break and gala lunch. Scientists, Research fellows and Students can join the EuroSciCon as an international member to receive discounts on registration. So come and join leading experts and allied professionals from August 22-23,2022 at Singapore City to keep up with the rapidly accelerating pace of change that is already having an effect on the field of Proteomics, Genomics & Bioinformatics.
WHY TO ATTEND?
Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics conference is a one of a kind meeting to unite overall acknowledged scholastics in the field of science and bioinformatics, Proteomics specialists, general wellbeing experts, researchers, scholarly researchers, industry analysts, researchers to deal with best in class research and innovations. Point of this meeting is invigorating new techniques bringing about high throughput proteins & genes over the range. A Unique Opportunity for Advertisers and Sponsors at this International programme.
ABOUT SINGAPORE
Singapore, city, capital of the Republic of Singapore. It is located at the southern part of Singapore Island. Its tactical position at strait between the Indian Ocean and South China Sea, accompanied by its deepwater harbour, has made it the largest port in Southeast Asia and one of the world’s greatest commercial centres. The city, once a marked entity, so came to dominate the island that the Republic of Singapore.
SESSIONS/TRACKS

Bioinformatics is the field of science in which biology, computer science, and information technology merge to form a single discipline. The ultimate goal of the field is to enable the discovery of new biological insights as well as to create a global perspective from which unifying principles in biology can be discerned. At the beginning of the "genomic revolution," a bioinformatics concern was the creation and maintenance of a database to store biological information, such as nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Development of this type of database involved not only design issues, but the development of complex interfaces whereby researchers could both access existing data as well as submit new or revised data. Ultimately, however, all of this information must be combined to form a comprehensive picture of normal cellular activities so that researchers may study how these activities are altered in different disease states. Therefore, the field of bioinformatics has evolved such that the most pressing task now involves the analysis and interpretation of various types of data, including nucleotide and amino acid sequences, protein domains, and protein structures.
A more global perspective in experimental design; and the ability to capitalize on the emerging technology of database-mining--the process by which testable hypotheses are generated regarding the function or structure of a gene or protein of interest by identifying similar sequences in better characterized organisms.
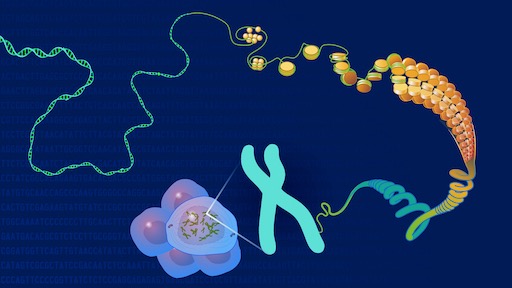
Genomics, in contrast, is the study of the entirety of an organism's genes – called the genome. Using high-performance computing and math techniques known as bioinformatics, genomics researchers analyze enormous amounts of DNA-sequence data to find variations that affect health, disease or drug response.
2.a) Structural Genomics
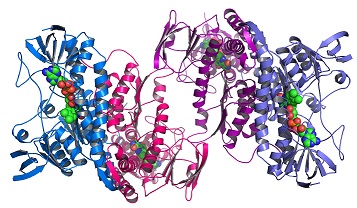
Structural genomics is the study of three-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by genes. It includes the genetic and physical mapping and sequencing of the whole genome. The main aim of structural genomics is to solve the experimental structures of all possible protein folds.
2.b) Functional Genomics

Functional genomics deals with the structure, function, and regulation of all genes rather than the single gene of the genome and dynamic aspects such as gene transcription, translation, and protein–protein interactions.The aim of functional genomics is to relate the complex relationship between genotype and phenotype at the genome level. Functional genomics gives an idea to understand the time and place where genes will express in different subtypes of cells, level of gene expression, gene expression regulation, and interaction of genes and its product, changes in gene expression during the onset of various diseases, and functional roles of different genes in cellular processes.
2.c) Comparative Genomics

Comparative genomics is a field of biological research in which the genome sequences of different species — human, mouse, and a wide variety of other organisms from bacteria to chimpanzees — are compared. By comparing the sequences of genomes of different organisms, researchers can understand what, at the molecular level, distinguishes different life forms from each other. Comparative genomics also provides a powerful tool for studying evolutionary changes among organisms, helping to identify genes that are conserved or common among species, as well as genes that give each organism its unique characteristics.
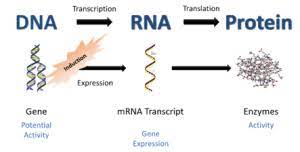
The field of proteomics is particularly important because most diseases are manifested at the level of protein activity. Consequently, proteomics seeks to correlate directly the involvement of specific proteins, protein complexes and their modification status in a given disease state.
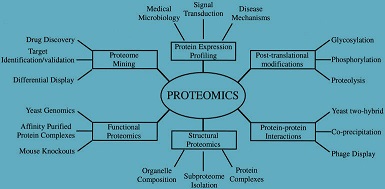
Expression proteomics involve the analysis of protein expression at a larger scale. It helps to identify main protein in a particular sample, and those protein differentially expressed in related samples—such as diseased vs. healthy tissue. If a protein is found only in a diseased sample then it can be a useful drug target or diagnostic marker. Proteins with the same or similar expression profiles may also be functionally related. There are technologies such as 2D-PAGE and mass spectrometry that are used in expression proteomics.

Functional proteomics constitutes an emerging research area in the proteomic field focused to two major targets, the elucidation of biological function of unknown proteins and the definition of cellular mechanisms at the molecular level. Understanding protein functions as well as unravelling molecular mechanisms within the cell are then depending on the identification of the interacting protein partners.
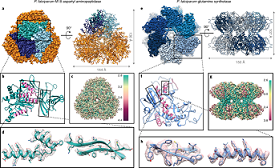
The ultimate aim of structural proteomics is to detemine the structure of all proteins in a cell or organism. Structural Proteomics approaches have led to different thousands of protein structures being determined and put into the protein data bank (PDB).
The offerings of Structural Proteomics to Understand the Function of Hypothetical Proteins. Developments in structural genomics have led to the automation of protein production and rose to the structure determination pipeline, resulting in a quick increase in the number of new protein structures.
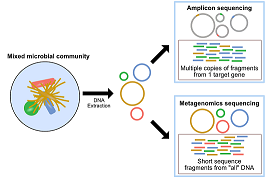
Metagenomics is the study of genomic content that recovered directly from environmental samples. There are two basic types of Metagenomics studies.a)Metagenomics based on sequencing and analysis of DNA from environmental samples b)Metagenomics based on screening of particular function or activityThe study of Metagenomic explored many novel microbial genes that are involved in the metabolism like energy acquisition, carbon, and nitrogen metabolism in natural environments. Metagenomics, based on sequencing, is applied to explore the structure of genome, identify the novel genes, and compare the organism genomes of different communities to establish the degree of diversity.
Transcriptomics is the study of the transcriptome—the complete set of RNA transcripts that are produced by the genome, under specific circumstances or in a specific cell—using high-throughput methods, such as microarray analysis. Comparison of transcriptomes allows the identification of genes that are differentially expressed in distinct cell populations, or in response to different treatments. Transcriptomic Data Analysis involves characterization of all transcriptional activity (coding and non-coding), or a select subset of RNA transcripts within a given sample. The analysis of transcriptomes allows the identification of candidate genes and expressed markers associated with traits of interest.
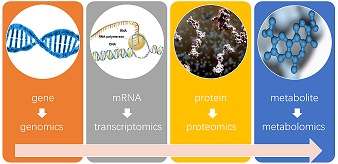
Metabolomics, which is defined as the comprehensive analysis of metabolites in a biological specimen, is an emerging technology that holds promise to inform the practice of precision medicine. Metabolomics is an analytical profiling technique for measuring and comparing large numbers of metabolites present in biological samples. Combining high-throughput analytical chemistry and multivariate data analysis, metabolomics offers a window on metabolic mechanisms.
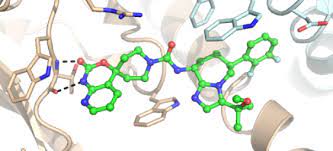
Molecular modelling is based on the development of theoretical and computational methodologies, to model and study the behaviour of molecules, from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. Molecular models typically describe atoms (nucleus and electrons collectively) as point charges with an associated mass. The interactions between neighbouring atoms are described by spring-like interactions (representing chemical bonds) and Van der Waals forces.
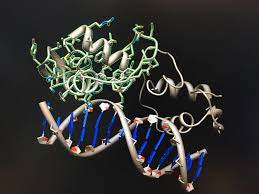
Structural bioinformatics is the branch of bioinformatics that is related to the analysis and prediction of the three-dimensionalstructure of biological macromolecules such as proteins, RNA, and DNA. It deals with generalizations about macromolecular 3D structures such as comparisons of overall folds and local motifs, principles of molecular folding, evolution, binding interactions, and structure/function relationships, working both from experimentally solved structures and from computational models.

In bioinformatics, methods of pathway analysis might be used to identify key genes/ proteins within a previously known pathway in relation to a particular experiment / pathological condition or building a pathway de novo from proteins that have been identified as key affected elements. IPA is a web-based bioinformatics application that allows researchers to upload data analysis results from high-throughput experiments such as microarray and next generation sequencing for functional analyze, integration, and further understanding.
Market Analysis
Bioinformatics is the combination of biology and information technology. It is used widely in the management of biological information in the field of medical research and the development of drugs. It uses computer software tools for database creation, data management, data warehousing, data mining, and communication networking. Expenditure and investments in drug discovery are mounting the market growth. Inclination towards collaborating with genetics research organizations is the key element responsible for the large market share of medical biotechnology. The field covers many advanced and specialized areas of life such as structural genomics, functional genomics, DNA microarrays, comparative genomics, medical information, and others. The rising need for integrated bioinformatics systems in proteomics and genomics also supports the growth of the bioinformatics market. Genomics is the largest application-based bioinformatics market. Increasing mergers and acquisitions and new product innovation are some of the latest trends in the bioinformatics market. Nanopore sequencing technology is one of the growth opportunities for the bioinformatics market. Lack of skilled professionals and high costs for implementation of bioinformatics software are restraining the growth of the bioinformatics market.






















